[Behavioral Pattern] 책임 연쇄 패턴 (Chain of Responsibility Pattern)
Design Pattern / Behavioral Pattern
책임 연쇄 패턴의 정의와 해당 디자인 패턴의 예제 코드를 통한 이해 및 설명 정리
개념
객체들이 연결된 체인 형태로 존재하며, 각 객체가 요청을 처리하지 못할 경우, 다음 객체에게 책임을 전달하고, 다음 객체 또한 처리하지 못하면 다시 다음 객체로 전달하는 패턴
객체 간의 결합도를 낮추고, 요청을 처리할 객체를 동적으로 결정하는 데 유용함
- 요청 처리 과정에서 요청을 처리할 객체를 직접 지정하지 않아도 되므로, 클라이언트 코드와 서버 코드 간의 결합도가 낮아짐
예를 들어 로그인 처리나 예외 처리와 같은 경우에 유용하게 사용될 수 있음
요청 처리 과정에서 각 객체가 책임을 나누어 처리할 수 있으므로, 코드 유지 보수성과 확장성을 높일 수 있음
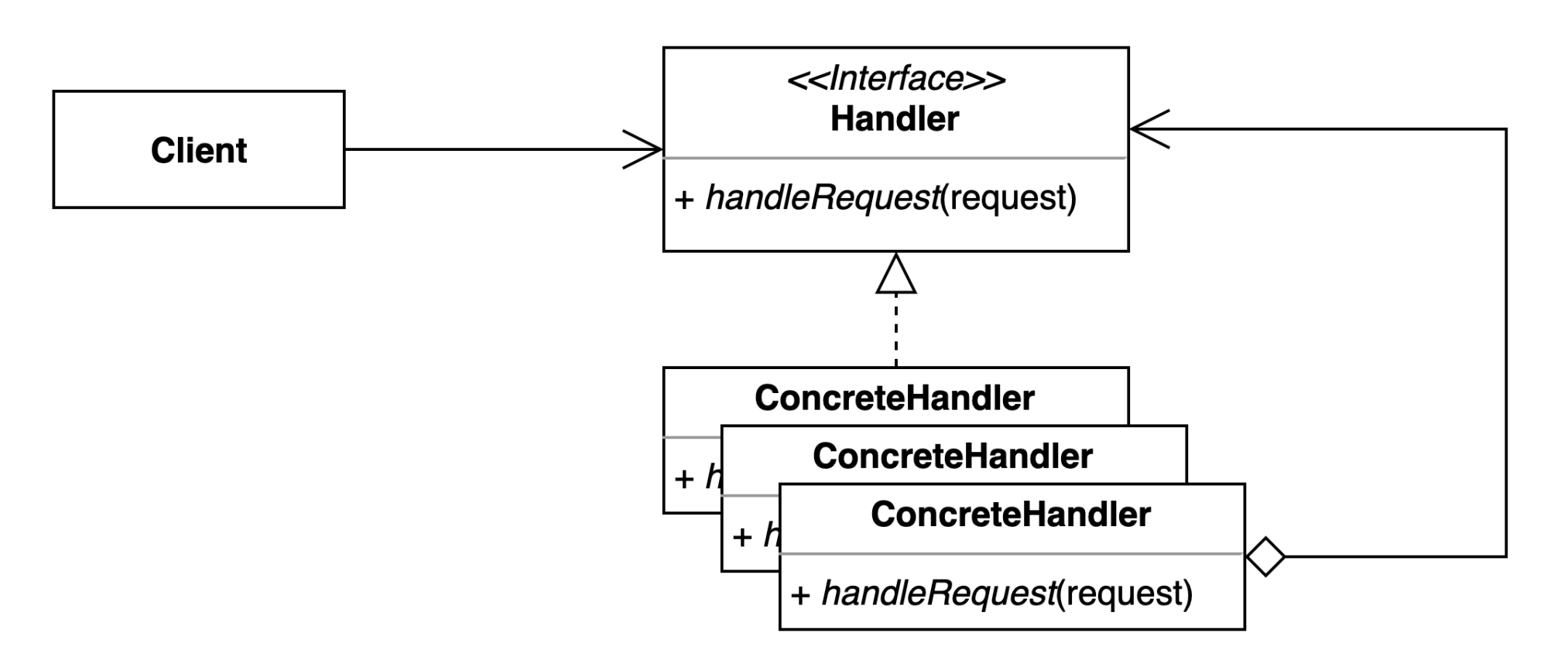
패턴 구조
Handler- 요청을 수신하고 처리 객체들의 집합을 정의하는 인터페이스
ConcreteHandler요청을 처리하는 실제 처리 객체
핸들러에 대한 필드를 내부에 가지고 있으며, 메서드를 통해 다음 핸들러를 체인시키고 다음 체인의 핸들러를 바라봄
자신이 처리할 수 없는 요구가 나오면, 바라보고 있는 다음 체인의 핸들러에게 요청을 떠넘김
ConcreteHandler_1-ConcreteHandler_2-ConcreteHandler_3- … 이와 같은 방식으로 체인 형식이 구성됨
Client- 요청을 핸들러에게 전달
예제 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// 구체적인 핸들러를 묶는 인터페이스 (추상 클래스)
abstract class Handler {
// 다음 체인으로 연결될 핸들러
protected nextHandler: Handler | null = null;
// 생성자를 통해 연결시킬 핸들러를 등록
public setNext(handler: Handler): Handler {
this.nextHandler = handler;
return handler; // 메서드 체이닝 구성을 위해 인자를 그대로 반환함
}
// 자식 핸들러에서 구체화하는 추상 메서드
protected abstract process(url: string): void;
// 핸들러가 요청에 대해 처리하는 메서드
public run(url: string): void {
this.process(url);
// 만일 핸들러가 연결된게 있다면 다음 핸들러로 책임을 떠넘김
if (this.nextHandler !== null) {
this.nextHandler.run(url);
}
}
}
export { Handler };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import { Handler } from "./handler";
class ProtocolHandler extends Handler {
protected override process(url: string): void {
const index: number = url.indexOf("://");
if (index !== -1) {
console.log(`PROTOCOL : ${url.substring(0, index)}`);
} else {
console.log("NO PROTOCOL");
}
}
}
export { ProtocolHandler };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
import { Handler } from "./handler";
class DomainHandler extends Handler {
protected override process(url: string): void {
const startIndex: number = url.indexOf("://");
const lastIndex: number = url.lastIndexOf(":");
if (startIndex === -1) {
if (lastIndex === -1) {
console.log(`DOMAIN : ${url}`);
} else {
console.log(`DOMAIN : ${url.substring(0, lastIndex)}`);
}
} else if (startIndex !== lastIndex) {
console.log(`DOMAIN : ${url.substring(startIndex + 3, lastIndex)}`);
} else {
console.log(`DOMAIN : ${url.substring(startIndex + 3)}`);
}
}
}
export { DomainHandler };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
import { Handler } from "./handler";
class PortHandler extends Handler {
protected override process(url: string): void {
const index: number = url.lastIndexOf(":");
if (index !== -1) {
const strPort: string = url.substring(index + 1);
try {
const port: number = Number.parseInt(strPort);
console.log("PORT : " + port);
} catch (error: any) {
console.error(error);
}
}
}
}
export { PortHandler };
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
import { ProtocolHandler } from "./concrete_handler_1";
import { DomainHandler } from "./concrete_handler_2";
import { PortHandler } from "./concrete_handler_3";
import { Handler } from "./handler";
class Client {
public static main(_args?: string[]): void {
// 1. 핸들러 생성
const handler_1: Handler = new ProtocolHandler();
const handler_2: Handler = new DomainHandler();
const handler_3: Handler = new PortHandler();
// 2. 핸들러 연결 설정 (handler_1 - handler_2 - handler_3)
handler_1.setNext(handler_2).setNext(handler_3);
// 3. 요청에 대한 처리 연쇄 실행
const url_1 = "http://www.youtube.com:443";
console.log(`INPUT : ${url_1}`);
handler_1.run(url_1);
console.log("");
const url_2 = "https://hyungjinhan.vercel.app:3000";
console.log(`INPUT : ${url_2}`);
handler_1.run(url_2);
console.log("");
const url_3 = "http://localhost:8080";
console.log(`INPUT : ${url_3}`);
handler_1.run(url_3);
}
}
Client.main();
// INPUT : http://www.youtube.com:443
// PROTOCOL : http
// DOMAIN : www.youtube.com
// PORT : 443
// INPUT : https://hyungjinhan.vercel.app:3000
// PROTOCOL : https
// DOMAIN : hyungjinhan.vercel.app
// PORT : 3000
// INPUT : http://localhost:8080
// PROTOCOL : http
// DOMAIN : localhost
// PORT : 8080
참고한 출처 사이트
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.