[Behavioral Pattern] 방문자 패턴 (Visitor Pattern)
Design Pattern / Behavioral Pattern
방문자 패턴의 정의와 해당 디자인 패턴의 예제 코드를 통한 이해 및 설명 정리
개념
방문자 패턴이란 계층을 가진 클래스들에서 특정 알고리즘을 캡슐화하고 싶을 때 사용
이를 통해서 여러 계층에서 쓰이는 알고리즘을 쉽게 전환하고 확장이 가능
다소 복잡할 수 있지만, 사실 상태 패턴이나 전략 패턴에서
Context가 여러 계층으로 바뀐 것이라고 보면 쉬움
계층이 여러 개이기 때문에
Strategy혹은State에서 수행할 메소드가 계층의 모든 타입에 오버로딩되어야 하고, 오버로딩의 정적 바인딩 문제를 해결하기 위해서 계층별로accept함수를 생성위의 과정으로 통해
State나Strategy처럼 캡슐화된 부분은 유연해지나,Context의 확장이 어려운 편기능들이 많아질수록 복잡해지며 적용 범위가 좁기 떄문에 매우 일반적인 패턴은 아니며, 사용에 있어서 인기도가 높지 않음
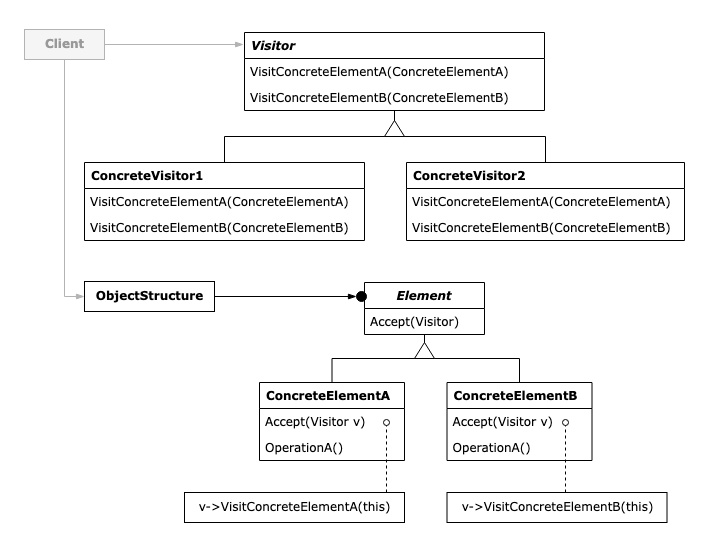
패턴 구조
Visitor- 데이터 구조 내 각각의 구체적인 요소에
visit메소드를 선언
- 데이터 구조 내 각각의 구체적인 요소에
ConcreteVisitorVisitor인터페이스를 구현하고,ConcreteElement역할을 처리
ElementVisitor역할이 방문할 곳을 나타내는 역할을 함방문자를 받아들이는
element메소드를 선언
ConcreteElementElement인터페이스를 구현하는 역할
ObjectStructureElememt역할의 집합을 취급하는 역할
예제 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
interface Component {
accept(visitor: Visitor): void;
}
class ConcreteComponentA implements Component {
public accept(visitor: Visitor): void {
visitor.visitConcreteComponentA(this);
}
public exclusiveMethodOfConcreteComponentA(): string {
return "A";
}
}
class ConcreteComponentB implements Component {
public accept(visitor: Visitor): void {
visitor.visitConcreteComponentB(this);
}
public speccialMethodOfConcreteComponentB(): string {
return "B";
}
}
interface Visitor {
visitConcreteComponentA(element: ConcreteComponentA): void;
visitConcreteComponentB(element: ConcreteComponentB): void;
}
class ConcreteVisitor1 implements Visitor {
public visitConcreteComponentA(element: ConcreteComponentA): void {
console.log(
`${element.exclusiveMethodOfConcreteComponentA()} + ConcreteVisitor1`
);
}
public visitConcreteComponentB(element: ConcreteComponentB): void {
console.log(
`${element.speccialMethodOfConcreteComponentB()} + ConcreteVisitor1`
);
}
}
class ConcreteVisitor2 implements Visitor {
public visitConcreteComponentA(element: ConcreteComponentA): void {
console.log(
`${element.exclusiveMethodOfConcreteComponentA()} + ConcreteVisitor2`
);
}
public visitConcreteComponentB(element: ConcreteComponentB): void {
console.log(
`${element.speccialMethodOfConcreteComponentB()} + ConcreteVisitor2`
);
}
}
function clientCode(components: Component[], visitor: Visitor) {
for (const component of components) {
component.accept(visitor);
}
}
const components = [new ConcreteComponentA(), new ConcreteComponentB()];
console.log(
"The client code works with all visitors via the base Visitor interface:"
);
const visitor1 = new ConcreteVisitor1();
clientCode(components, visitor1);
console.log("");
console.log(
"It allows the sane client code to work with different types of visitors:"
);
const visitor2 = new ConcreteVisitor2();
clientCode(components, visitor2);
참고한 출처 사이트
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.